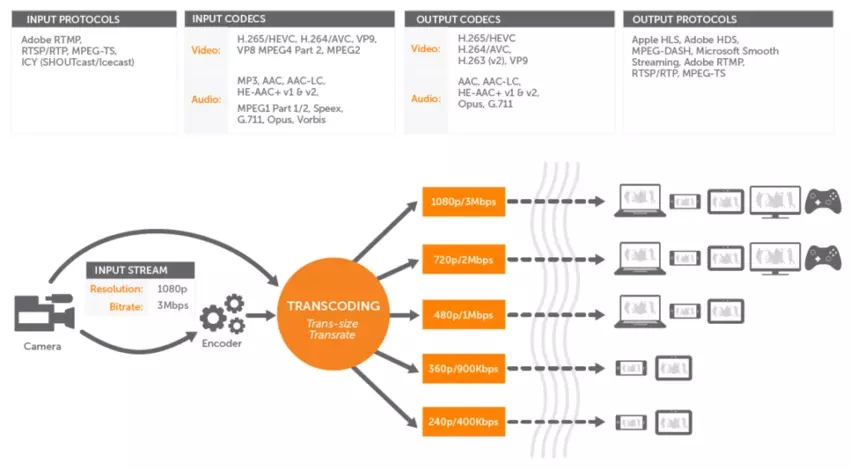
Video Transcoding also is known as Video Encoding is the process of converting a video from one video format to another. For example: Converting from .wmv file type to .mp4 file type.
Video Transcoding is usually done so that the transcoded video meets a particular device requirement and plays smoothly in that device.
HTTP Live Streaming (HLS)
HLS was first created by Apple Inc. as part of its QuickTime, Safari, OS X, and iOS software, which was later implemented by Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox and some versions of Google Chrome. Apple initially developed it to provide an alternative to Flash video.
While streaming a video using HLS, the video is broken down into multiple small chunks of videos and every small chunk of the video is encoded at different bit rates. All the chunks of videos are then finally sent to the client in the m3u8 file extension.
Hence HSL makes it possible to be streamed easily by a wide range of devices and also it makes sure that the videos are streamed in High Quality.
Cincopa videos work on HTML5 and use HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) protocol to stream its video to its users.
So, how to make this awesome technology work for your online video content?
Actually, you don’t even have to care about the technical side because Cincopa does it for you. Our all-new HTML5 video player supports HLS streaming and guarantees flawless video playback on any device.
Cincopa’s video player is fully responsive, which means it’s adjusted automatically to particular screen size. As always, our online video loads fast and offers a solid customization toolset to your option.
Cincopa’s live video streaming platform lets you deliver videos to viewers worldwide from a single managing dashboard. Due to HTTP live streaming (HLS) technology that lies at the root of our service you’re enabled to reach your audience on any device.
Advantages of using HTTP Live Streaming?
1. Compatibility
Although Apple created HLS to work with QuickTime, Safari, OS X, and iOS software, now HLS is supported by almost all modern web browsers and devices, making it a device friendly protocol.
2. Cost-Efficient
Since HLS supports a wide range of devices and media source extensions. There’s no need to use a specific device to watch the content, which cuts down the extra cost of getting a device to watch. Standard web servers handle HLS streaming without any problem, reducing the cost of creating special servers.
3. High Quality
HLS delivers videos dynamically at the best possible quality which allows viewers to select playback quality up to 4K video and with none to minimal buffering or lagging. This approach leads to great user experience and
4. Great Security
HLS provides better security when compared to the popular Flash, which was widely used before HLS came into presence. HLS provides good security for the viewers who are watching the video and also after the video is streamed.
5. Adaptive Bitrates
HLS uses Adaptive bitrate streaming which is a technique used in streaming multimedia over computer networks. It works by detecting a real-time user’s internet bandwidth and CPU capacity. Then based on the result, adaptive bitrate streaming provides the quality of the video. This results in very little buffering, fast start time and good user experience for both high-end and low-end connections.
What Is an M3U8 File?
M3U8 is a file format that contains multimedia playlists and its content is ASCII text.
It is not a video format like WMV or MPEG, you won’t be able to open or play an m3u or m3u8 files in a player and hope to watch the video. M3U8 is the UTF-8 version m3u.
An m3u8 file specifies the locations of one or more media files, rather than the video itself. Therefore, an HLS player is required to download and play the actual video files.
There is one way you can open an M3U8 file online using HSLPlayer.net. However, HSLPlayer.net will not read the file if you have an M3U8 file in the local storage. You can only use HSLPlayer.net if you have a URL to the .M3U8 file and the files it references are also online.
The M3U8 file format works well with HLS, where it’s used to define media streams. In HLS there are two kinds of m3u8 files:
Media playlist: This type of file contains the URLs of the files needed for streaming (i.e. chunks of the original video to be played).
Master playlist: This type of file contains the URLs to media playlists which, in turn, contain variants of the same video prepared for different bandwidths.